Sep. 25, 2020

Guardicore has discovered FritzFrog, a sophisticated peer-to-peer (P2P) botnet which has been actively breaching SSH servers since January 2020. Golang-Based Malware: FritzFrog executes a worm malware which is written in Golang, and is modular, multi-threaded and fileless, leaving no trace on the infected machine’s disk. Actively Targeting Government, Education, Finance and more: FritzFrog has attempted to brute force and propagate to tens of millions of IP addresses of governmental offices, educational institutions, medical centers, banks and numerous telecom companies.
Nov. 14, 2018

A recently discovered botnet has taken control of an eye-popping 100,000 home and small-office routers made from a range of manufacturers, mainly by exploiting a critical vulnerability that has remained unaddressed on infected devices more than five years after it came to light. Researchers from Netlab 360, who reported the mass infection late last week, have dubbed the botnet BCMUPnP_Hunter. The name is a reference to a buggy implementation of the Universal Plug and Play protocol built into Broadcom chipsets used in vulnerable devices.
May. 26, 2018

In a public service announcement published Friday and noted by Ars Technica, and a new addition to aUS Department of Justice press release, the FBI explains that it’s hoping that your actions will help the US government destroy a botnet before a Russian hacking group, Sofacy, can harden the malware’s defenses. How would pressing a button on your router help, though? According to the FBI, rebooting your router will destroy the part of the malware that can do nasty things like spy on your activities, while leaving the install package intact.
May. 16, 2018
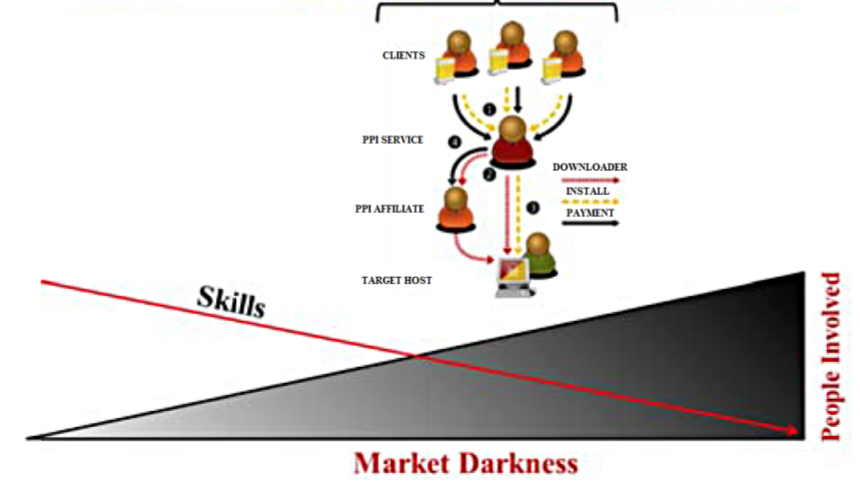
Botnets are shadowy networks of computers controlled by hidden actors and linked to everything thatâs bad on the web. They have been implicated in distributed denial-of-service attacks, spamming campaigns, click fraud, and bank fraud, to name just a few of the nastiest flavors of cybercrime. Clearly somebody, somewhere is making a fortune masterminding this kind of criminal activity.
Today we get an answer of sorts thank to the work of C.G.J. Putman at the University of Twente in the Netherlands and a couple of colleagues. âIt comes as no surprise that the primary motive for the use of botnets is for economic gain,â they say as they map out the costs and revenue streams. All that leads to a rough estimate of the cost of setting up a botnet on a national or international scale.
May. 12, 2018
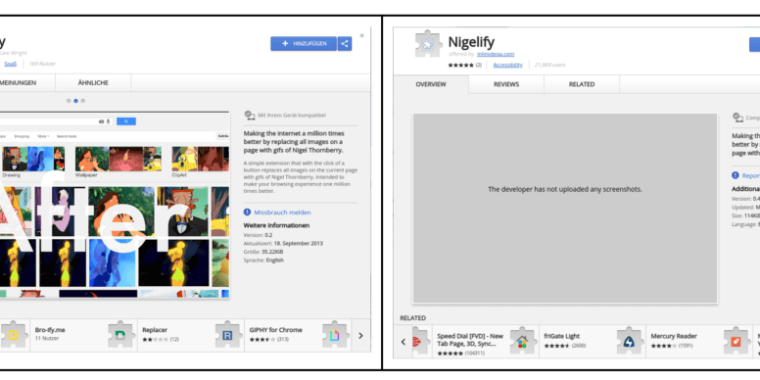
The extensions were being pushed in links sent over Facebook that led people to a fake YouTube page that asked for an extension to be installed. Once installed, the extensions executed JavaScript that made the computers part of a botnet. The botnet stole Facebook and Instagram credentials and collected details from a victim’s Facebook account.
The botnet then used that pilfered information to send links to friends of the infected person. Those links pushed the same malicious extensions. If any of those friends followed the link, the whole infection process started all over again.
May. 10, 2018

Within just 10 days of the disclosure of two critical vulnerabilities in GPON router at least 5 botnet families have been found exploiting the flaws to build an army of million devices. Security researchers from Chinese-based cybersecurity firm Qihoo 360 Netlab have spotted 5 botnet families, including Mettle, Muhstik, Mirai, Hajime, and Satori, making use of the GPON exploit in the wild. As detailed in our previous post, Gigabit-capable Passive Optical Network (GPON) routers manufacturer by South Korea-based DASAN Zhone Solutions have been found vulnerable to an authentication bypass (CVE-2018-10561) and a root-RCE (CVE-2018-10562) flaws that eventually allow remote attackers to take full control of the device.
May. 10, 2018

Security researchers have discovered the first IoT botnet malware strain that can survive device reboots and remain on infected devices after the initial compromise. This is a major game-changing moment in the realm of IoT and router malware. Until today, equipment owners could always remove IoT malware from their smart devices, modems, and routers by resetting the device.
May. 6, 2018

This attack relies on the file:// protocol to load and execute a remote script from a samba (SMB) share. This is noteworthy because typically the attachment is used as a downloader, but instead here we see one additional step that pushes this function one degree further thanks to the .url shortcut.
Source: malwarebytes.com
Apr. 24, 2018

Researchers are warning a recently discovered and highly critical vulnerability found inDrupal’s CMS platform is now being actively exploited by hackers who are using it to install cryptocurrency miners and to launch DDoS attacks via compromised systems. At the time of the disclosure, last month, researchers said they were not aware of any public exploits.
Source: threatpost.com
Mar. 20, 2018

This series of posts recounts how, in November 2016, we hunted for and took down Gooligan, the infamous Android OAuth stealing botnet. What makes Gooligan special is its weaponization of OAuth tokens, something that was never observed in mainstream crimeware before. At its peak, Gooligan had hijacked over 1M OAuth tokens in an attempt to perform fraudulent Play store installs and reviews.
Mar. 7, 2018
Gozi ISFB is a well-known and widely distributed banking trojan, and has been in the threat landscape for the past several years. Banking trojans are a widely distributed type of malware that attackers leverage in an attempt to obtain banking credentials from customers of various financial institutions. The source code associated with Gozi ISFB has been leaked several times over the years, and the robust features available within the Gozi ISFB code base have since been integrated into additional malware, such as GozNym.










