Cyber security news and services
Google Just Gave 2 Billion Chrome Users A Reason To Switch To Firefox

Google is planning to restrict modern ad blocking Chrome extensions to enterprise users only, according to 9to5Google. This is despite a backlash to an announcement by Googlein January proposing changes that will stop current ad blockers from working efficiently. And the software giant is not backing down: It says the only people that can use ad blockersfollowing the change will be Google’s enterprise users.
…Docker Bug Allows Root Access to Host File System

All of the current versions of Docker have a vulnerability that can allow an attacker to get read-write access to any path on the host server. The weakness is the result of a race condition in the Docker software and while there’s a fix in the works, it has not yet been integrated. The bug is the result of the way that the Docker software handles some symbolic links, which are files that have paths to other directories or files.
…Stolen NSA hacking tool now victimizing US cities

A hacking tool developed by the US National Security Agency is now being used to shut down American cities and towns, says a Saturday report in The New York Times. Code-named EternalBlue, the hacking exploit involves malicious software and was leaked in 2017 by a group called Shadow Brokers. Hackers used the tool that same year in the worldwide WannaCry ransomware attacks, which locked up computer systems at hospitals, banks and phone companies and required a ransom to set the networks free.
…First official version of Tor Browser for Android released on the Play Store

Today, the Tor Project released on the Google Play Store the first stable version of the Tor Browser for Android. This new mobile browser integrates the Tor protocol stack into a standalone browser and replaces Orfox as the main way to navigate the Tor network from an Android device. Tor Project developers have been working on this browser for eight months now, since September 2018, when they first released an alpha version for public testing.
…Baltimore ransomware nightmare could last weeks more, with big consequences

It’s been nearly two weeks since the City of Baltimore’s networks were shut down in response to a ransomware attack, and there’s still no end in sight to the attack’s impact. It may be weeks more before the city’s services return to something resembling normal—manual workarounds are being put in place to handle some services now, but the city’s water billing and other payment systems remain offline, as well as most of the city’s email and much of the government’s phone systems. The ransomware attack came in the midst of a major transition at City Hall.
…San Francisco just banned facial-recognition technology
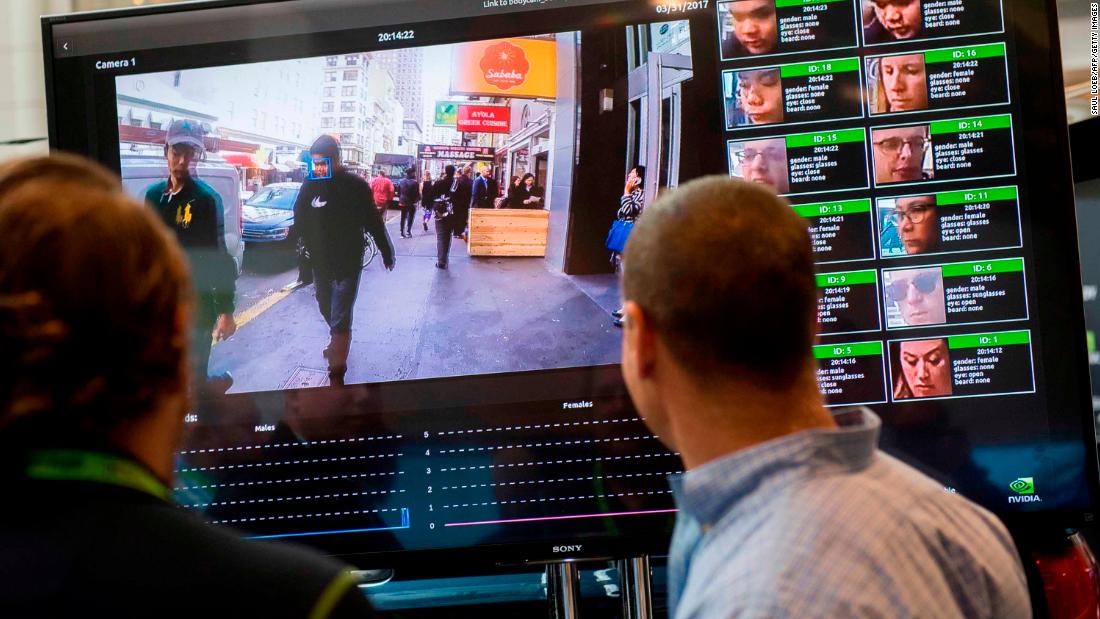

San Francisco, long one of the most tech-friendly and tech-savvy cities in the world, is now the first in the US to prohibit its government from using facial-recognition technology. The ban is part of a broader anti-surveillance ordinance that the city’s Board of Supervisors approved on Tuesday. The ordinance, which outlaws the use of facial-recognition technology by police and other government departments, could also spur other local governments to take similar action.
…Google pulls Huawei’s Android license

Following the US crackdown on Chinese technology companies, Google has cut off Huawei’s Android license, dealing a huge blow to the besieged phonemaker. Reuters first reported the news, and The Verge subsequently confirmed Google’s suspension of business with Huawei with a source familiar with the matter. Reached for comment, a Google spokesperson said only “We are complying with the order and reviewing the implications.”
The order, in this case, appears to be the US Commerce Department’s recent decision to place Huawei on the “Entity List,” which as Reuters reports is a list of companies that are unable to buy technology from US companies without government approval. Speaking to Reuters, a Google spokesperson confirmed that “Google Play and the security protections from Google Play Protect will continue to function on existing Huawei devices.” So while existing Huawei phones around the world won’t be immediately impacted by the decision, the future of updates for those phones as well as any new phones Huawei would produce remains in question.
…Google’s Sensorvault Is a Boon for Law Enforcement. This Is How It Works.

Law enforcement officials across the country have been seeking information from a Google database called Sensorvault — a trove of detailed location records involving at least hundreds of millions of devices worldwide, The New York Times found. Though the new technique can identify suspects near crimes, it runs the risk of sweeping up innocent bystanders, highlighting the impact that companies’ mass collection of data can have on people’s lives. Why does Google have this data?The Sensorvault database is connected to a Google service called Location History.
…Post-mortem and remediations for Apr 11 security incident
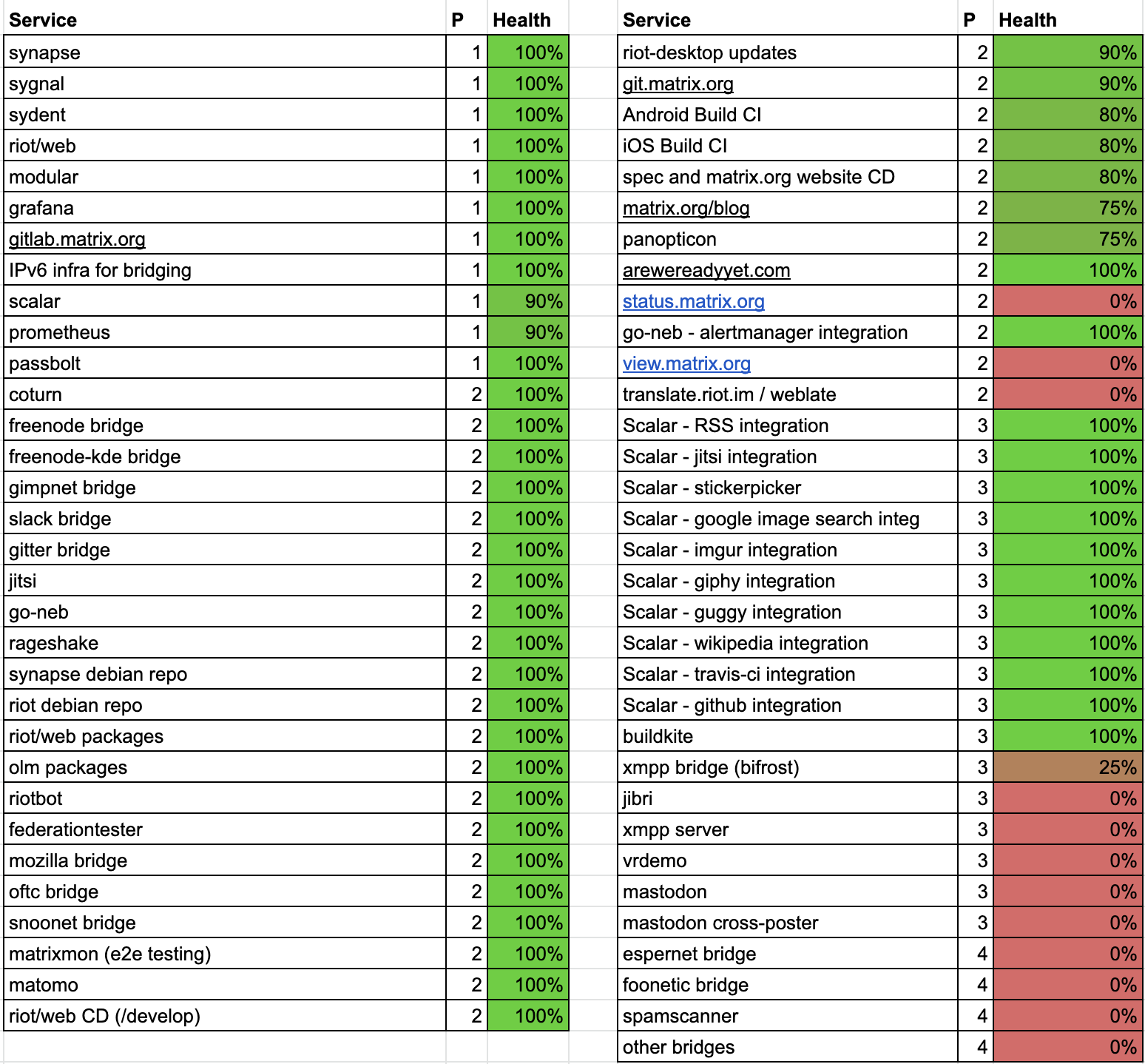
On April 11th we dealt with a major security incident impacting the infrastructure which runs the Matrix.org homeserver – specifically: removing an attacker who had gained superuser access to much of our production network. We provided updates at the time as events unfolded on April 11 and 12 via Twitter and our blog, but in this post weâll try to give a full analysis of what happened and, critically, what we have done to avoid this happening again in future.
…A serious hack hit WhatsApp

A security flaw in WhatsApp’s audio calling feature let hackers install spyware on iPhones and Androids. The attack is expected to have a limited reach but you should update WhatsApp straight away WhatsApp’s default end-to-end encryption is one of Facebook’s biggest security assets – but even this doesn’t help when the app itself is attacked. Mark Zuckerberg’s company has found a sophisticated cyberattack has been used to exploit a weakness in the messaging app that’s used by more than 1.5 billion people worldwide.
…Google Titan Security Key Recalled After Bluetooth Pairing Bug

Google’s Titan Security Key, launched in the U.S. market last August, is a USB dongle that offers an added layer of security features for Google accounts, such as two-factor authentication and protections from phishing attacks. Specifically impacted is the version of the Titan Security Key with Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) – not the NFC version of the security keys. The vulnerability stems from a misconfiguration in the Titan Security Keys’ Bluetooth pairing protocols, said Brand.
…Cisco Service Provider, WebEx Bugs Offer Up Remote Code Execution

Cisco is warning of critical remote code-execution (RCE) vulnerabilities in the Cisco Prime Infrastructure (PI) and Evolved Programmable Network (EPN) Manager, which is used by telcos, mobile carriers, cable companies and ISPs to manage their hardware infrastructure. The vendor also issued estimated bug-fix dates for an unpatched, high-severity Secure Boot flaw that was disclosed on Monday; and addressed a high-severity flaw that would allow arbitrary code-execution on WebEx for Windows, Cisco’s widely deployed web conferencing and collaboration software. The newly disclosed critical issue consists of multiple vulnerabilities in the web-based management interface of the PI EPN manager, which could allow a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code with root privileges on the underlying operating system.
…Forbes Becomes Latest Victim of Magecart Payment Card Skimmer

The web skimming script was recently found stealing payment data on the websites of Forbes Magazine as well as seven others. The payment card-siphoning Magecart group has struck again; this time injecting web-skimming scripts into the subscription website for the Forbes print magazine (as well as a slew of others over the past week). The script, which has since been removed, was discovered on the subscription page of the Forbes Magazine website on Wednesday, scraping up the payment data of subscribers.
…Stack Overflow hacker went undetected for a week

The hacker who breached Stack Overflow last week managed to access data on user accounts, the company said today in an update on its investigation into a security breach it disclosed last night. The update comes to shed some light into what happened on the company’s servers last week, after Stack Overflow left many users scratching their heads when it posted a very short message on Thursday, announcing a severe breach of its production systems. While it initially said that there was no evidence of the hacker accessing user data, the company changed its statement today.
…Chinese state-sponsored hackers breached TeamViewer in 2016

The German newspaper Der Spiegel revealed that the software company behind TeamViewer was compromised in 2016 by Chinese hackers. According to the media outlet, Chinese state-sponsored hackers used the Winnti trojan malware to infect the systems of the Company.
The Winnti group was first spotted by Kaspersky in 2013, according to the researchersthe gang has been active since 2007. The gang is financially-motivated and was mostly involved in cyber espionage campaigns. The hackers were known for targeting companies in theonline gaming industry, the majority of the victims is located in Southeast Asia.
…Alpine Linux Docker Images Shipped for 3 Years with Root Accounts Unlocked

For three years, some Alpine Linux Docker images have shipped with a root account and no password, opening the door for attackers to easily access vulnerable servers and workstations provisioned for the images. Affected versions of Alpine Linux Docker distros include 3.3, 3.4, 3.5, 3.6, 3.7, 3.8 and 3.9 Alpine Docker Edge, according to Cisco Talos researchers who discovered the bug,tested each version and released their findings on Wednesday. Vulnerable images of Alpine Linux Dockers were available via the official Docker Hub portal since late 2015.
…Cisco Talos warns of hardcoded credentials in Alpine Linux Docker Images

Since December 2015, Alpine Linux Docker images have been shipped with hardcoded credentials, a NULL password for the root user. The NULL password for the root account was included in the Official Alpine Linux Docker images since v3.3. The bug received a CVSS score of 9.8, it affects Alpine Docker versions 3.3 to 3.9, including Alpine Docker Edge.
The issue wasfirst reported in August 2015 and patched in November, evidently, it was re-introducedin December 2015. The NULL passoword is present in the/etc/shadowfile of the affected builds of the Alpine Docker Image.
…How Chinese Spies Got the N.S.A.’s Hacking Tools, and Used Them for Attacks

Chinese intelligence agents acquired National Security Agency hacking tools and repurposed them in 2016 to attack American allies and private companies in Europe and Asia, a leading cybersecurity firm has discovered. The episode is the latest evidence that the United States has lost control of key parts of its cybersecurity arsenal. Based on the timing of the attacks and clues in the computer code, researchers with the firm Symantec believe the Chinese did not steal the code but captured it from an N.S.A. attack on their own computers — like a gunslinger who grabs an enemy’s rifle and starts blasting away.
…Cisco Warns of Critical Nexus 9000 Data Center Flaw

A critical vulnerability in Cisco’s software-defined networking (SDN) software could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to connect to a vulnerable data-center switch and take it over, with the privileges of the root user. The bug (CVE-2019-1804), which has a CVSS severity rating of 9.8 out of 10, exists in the Cisco Nexus 9000 Series Application Centric Infrastructure (ACI) Mode Switch Software, which is part of Cisco’s SDN approach. Enterprises use ACI to deploy and control applications across their infrastructure, including their multicloud footprints, with consistent policies – in theory boosting security and high availability.
…A hacker is wiping Git repositories and asking for a ransom

Hundreds of developers have had had Git source code repositories wiped and replaced with a ransom demand. The attacks started earlier today, appear to be coordinated across Git hosting services (GitHub, Bitbucket, GitLab), and it is still unclear how they are happening. What it is known is that the hacker removes all source code and recent commits from vitcims’ Git repositories, and leaves a ransom note behind that asks for a payment of 0.1 Bitcoin (~$570).
…